Topics 2023.05.10
Establishment of an industry-academia consortium to utilize SoftBank's original GNSS observation network
Precise measurement of crustal deformation associated with earthquakes and volcanic eruptions is fundamental to understanding these phenomena. The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is commonly used to measure these crustal deformations precisely. The position of the antenna receiving the signal can be determined precisely by measuring the distance between the GNSS antenna and the satellites. Furthermore, by examining changes in this position over time, it is possible to estimate the behavior of crustal deformation at the location where the antenna is installed. In Japan, the Geospatial Information Authority of Japan (GSI) has constructed about 1,300 continuous GNSS stations called the "GNSS Earth Observation Network System (GEONET)." The GEONET has provided many significant seismological and volcanological findings. In this manner, the GEONET plays a significant role as a reference to accurately determine the shape of Japanese Islands.
On the other hand, in recent years, private companies have been developing their own GNSS observation networks to provide advanced positioning services. For example, SoftBank Corp. (hereinafter referred to as "SoftBank") has deployed its own dense GNSS observation network of more than 3,300 stations nationwide to provide highly accurate positioning services.
The Graduate School of Science, Tohoku University, has quantitatively demonstrated for the first time that SoftBank's GNSS observation network can provide information on crustal deformation with roughly the same accuracy as the GSI's GEONET and that this network can contribute to understanding the source image of earthquakes and improving the long-term evaluation of earthquake occurrence on inland active faults. These results suggest that not only seismology and volcanology but also a wide range of earth science fields can utilize SoftBank's GNSS observation network, which is expected to complement GSI's GEONET and expand its use.
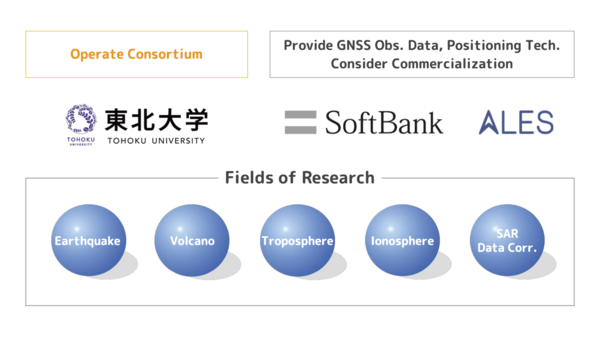
Based on these backgrounds, the Graduate School of Science, Tohoku University, in cooperation with SoftBank and ALES Corporation, established the "Consortium to utilize the SoftBank for Earth and Space Science" in August 2022, with the participation of the two companies and 18 departments from 12 research institutes in Japan. The consortium aims to verify how to utilize SoftBank's GNSS observation network in the earth science field. The consortium currently receives GNSS observation data from SoftBank and conducts feasibility studies in various earth science fields based on the data. The consortium expects to produce many future research results and contribute to disaster prevention and mitigation, such as highly accurate prediction of natural disasters based on these research results.
Yusaku Ohta (Associate Professor)
Research Center for Prediction of Earthquakes and Volcanic Eruptions